Technology DevelopmentIce Engineering
Through the development of icebreakers and other ice-going vessels and the research and development of the underlying technologies that support them, JMU provides functions essential for missions (observation, resource development support, transportation, etc.) in the so-called “polar regions” such as the Arctic and Antarctic.
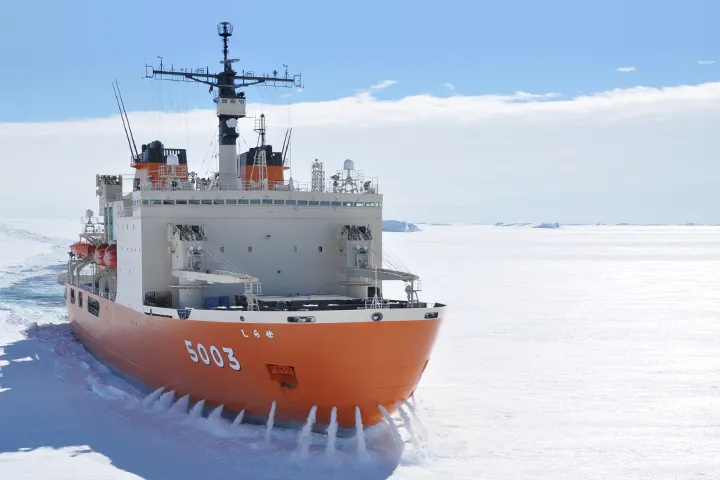

JMU was the first in the world to conduct research to balance the performance of breaking ice and the performance of navigating ice-free seas through advanced technology.
JMU is the only private company in Japan to have an “ice tank” that can reproduce the ice sea environment (As of January 2023).
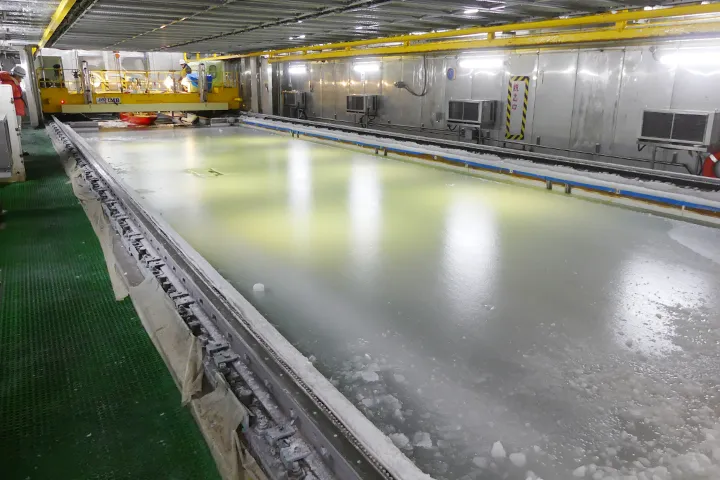
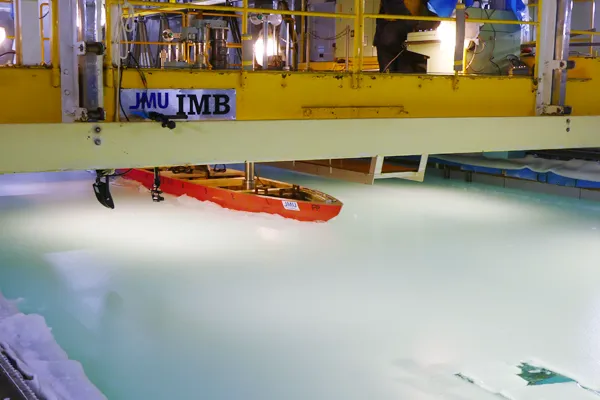
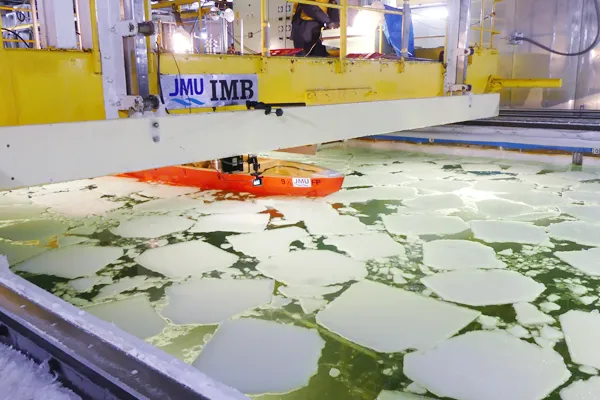
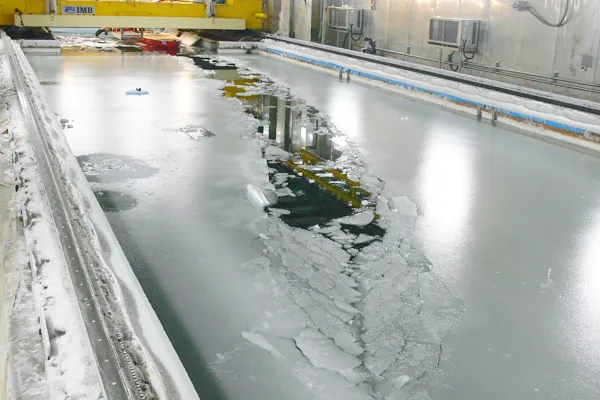




We are working on simulation technology for preliminary evaluation. In the future, we will incorporate advanced technologies and develop more advanced simulation technologies.
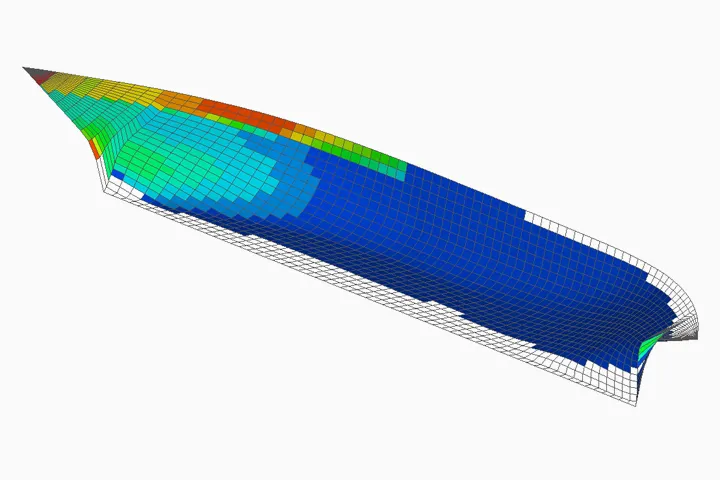
Numerical Calculation of Ice Resistance
We develop the icebreaker’s hull form by efficient use of the numerical simulation before conducting the ice tank tests. On the estimation of ice resistance, the resistance components due to ice-breaking, sinking broken ice, rotating broken ice and removing broken ice are calculated by 3D panel method. From these results we aim to make the ice resistance lower to improve hull form.
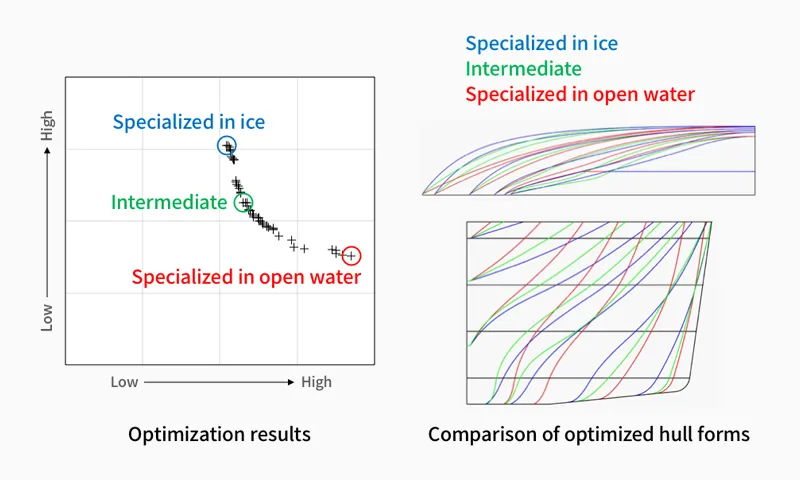
Optimization technology for icebreaking hull form
Depending on the application of the icebreaker, the performance balance will vary. Optimization calculations has made it possible to develop efficient hull forms. We are improving this method for actual operation.
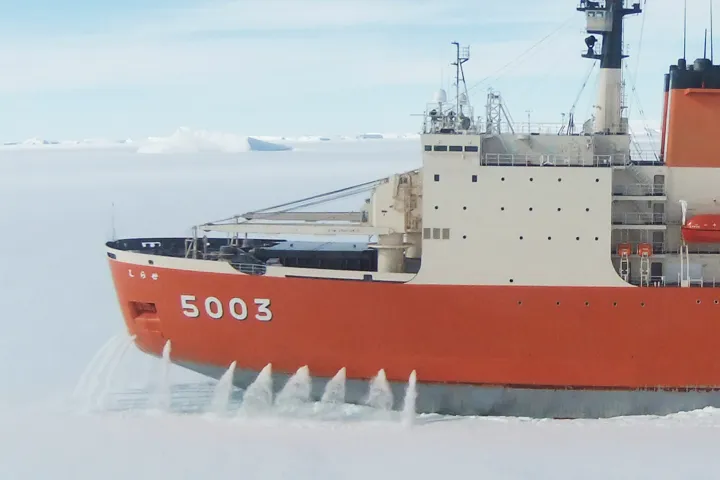
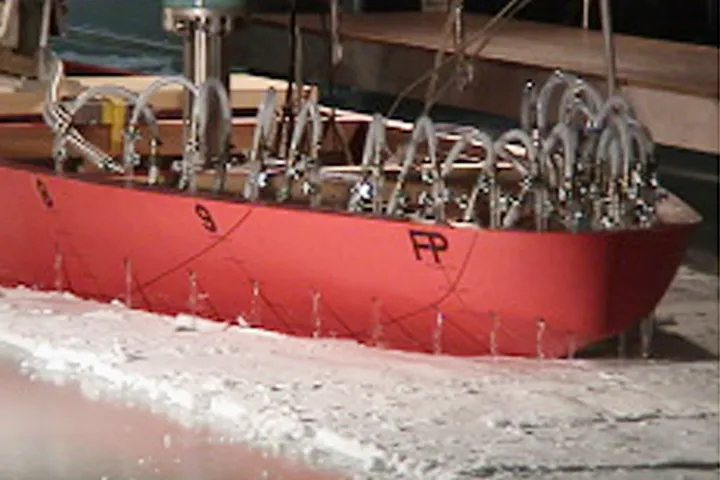
Reduction of Snow Resistance by Bow Water Flushing
Dry snow accumulated on sea ice surface increases icebreaking resistance. Especially, at ramming operation, the penetration distance becomes shorter due to the snow friction and the absorption of the kinetic energy like a damper.
The bow water flushing system sprays sea water, which is drawn from the ship bottom, on the accumulated dry snow and reduces the snow resistance by wetting. This system was applied to the Japanese Antarctic research icebreaker “Shirase (II)”.


Special Hull Form for Excellent Ice Removal Performance
We have designed the new hull form that accelerates removing broken ice pieces from the bottom of the ship. This hull form can reduce the friction resistance of ice pieces and the interaction between the propulsor and ice pieces. This design concept was applied to the Japanese Antarctic research icebreaker “Shirase (II)”, the icebreaking patrol ship, the icebreaking sightseeing vessel and so on.

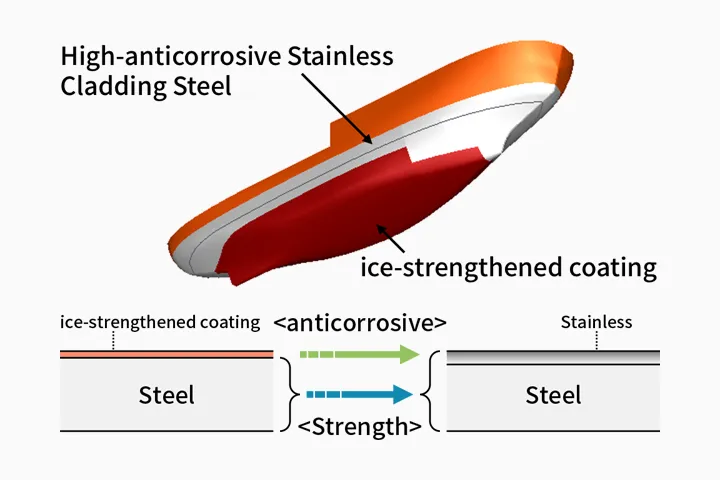
Application of Newly-developed High-anticorrosive Stainless Cladding Steel
Although ice-strengthened coating like solvent-free epoxy is hard to come off hull surface, the surface roughness becomes greater gradually through longtime contact with ice. JFE Steel Corporation has developed the new high-anticorrosive stainless cladding steel in order to keep the smooth surface of the icebreaker under the cooperation with JMU. This new material was applied to the Japanese Antarctic research icebreaker “Shirase (II)” and it showed the excellent anticorrosive performance.
Technology on Navigation Support in Ice-covered Water
Navigation in ice-covered water is affected by the ice condition change in area and season. We evaluate whether the ship performance is suitable or not from the viewpoint of economy and schedule planned in ice navigation by using the simulation program of ice navigation that we originally developed.
